Retina
RETINA jeopardizes your vision ...
WHAT IS RETINA?
It is made up of cells that allow the eye to see in color and colorless. It is a layer of the eye directly connected to the brain. Its thickness is 0.1-0.5 mm. The image formed in the retina is transmitted to the brain with 1 million nerve fibers (optic nerve). The reverse image occurred in the eye is interpreted in the brain.
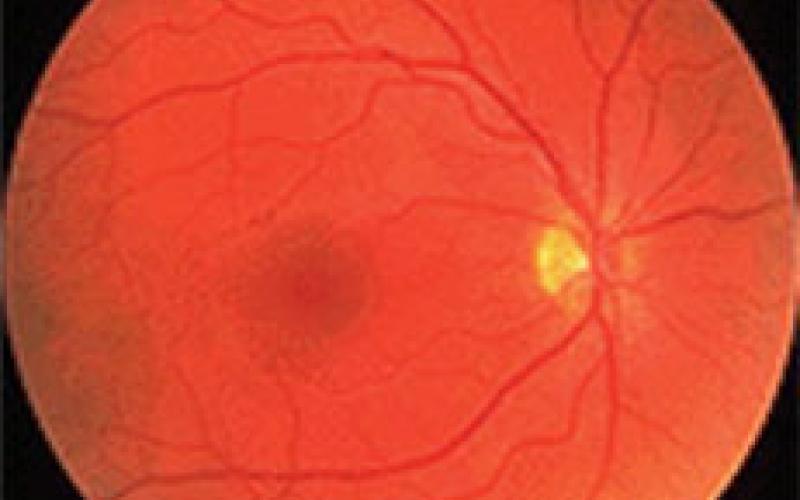
Normal Eye Ground Display

Retinal Vein Occlusion
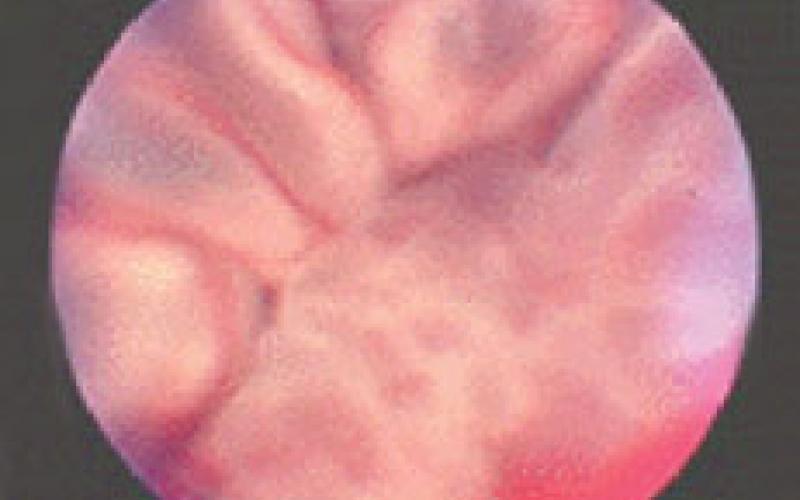
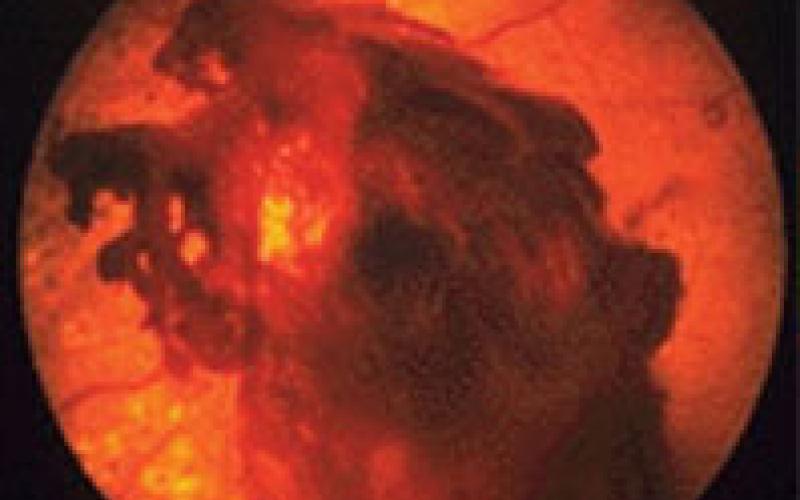
Retinal Detachment
WHO HAS THE RETINA DISEASES?
- Congenital (congenital)
- Hereditary
- AMD (age-related macular degeneration)
- Inflammatory diseases,
- Vascular (vascular),
- Disorders related to systemic diseases (hypertension, diabetes, collagenosis, etc.)
- Macular diseases (holding the center of vision)
- Retinal toxicity (drug-induced retinal damage)
- Tumors, retinal tears and holes, retinal detachment
MAIN SYMPTOMS
- Sudden or slow vision loss,
- Light flashes,
- Floating specks, objects circulating in sight, veiling of vision,
- Temporary and short-term vision loss,
- Dark areas in the field of view,
There may be no symptoms of retinal diseases.
It may cause loss of vision suddenly or slowly!
WHY IS EARLY DIAGNOSIS VERY IMPORTANT?
Retinal damage may not heal after occurrence since damaged retinal cells cannot regenerate.
WHAT ARE THE DIAGNOSIS AND EXAMINATION METHODS?
- Subjective: Medical history, visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, PAM (Potential Acuity Meter), visual field, Amsler card.
- Objective: Fundus examination (Direct and Indirect Ophthalmoscopy), FFA (Fundus Fluorescein Angiography), ICG (Indocyanin Green Angiography) Electrophysiological examinations (ERG, EOG etc.), OCT (laser tomography of the eye layers)

NORMAL FFA

Abnormal FFA
HOW TO TREAT?
The treatment types that can be applied according to the diagnosis;
- Medical Treatment (in some cases)
- ALT Laser (photocoagulation)
- Operation (vitreo-retinal surgery)
DIABETIC RETINOPATHY (DRP)
It is one of the most common causes of blindness in the world. Nearly 10 years after the onset of diabetes, sugar-induced eye disease occurs, which is a microangiopathy. Microangiopathy occurs in the form of blockages in the capillaries. In advanced stages, intraocular hemorrhage, band formation, retinal detachment may occur. After the level of vascular damage in the eye ground is determined by FFA, laser photocoagulation treatment is applied to the retina, if necessary. The patient should be examined every 3-6 months and angiography and laser should be repeated, if necessary. Vision lost in diabetes cannot be gained, the aim of laser treatment is to prevent blindness.
Even if you do not have any complaints, it is advisable to have an ophthalmological examination every six months at the latest.
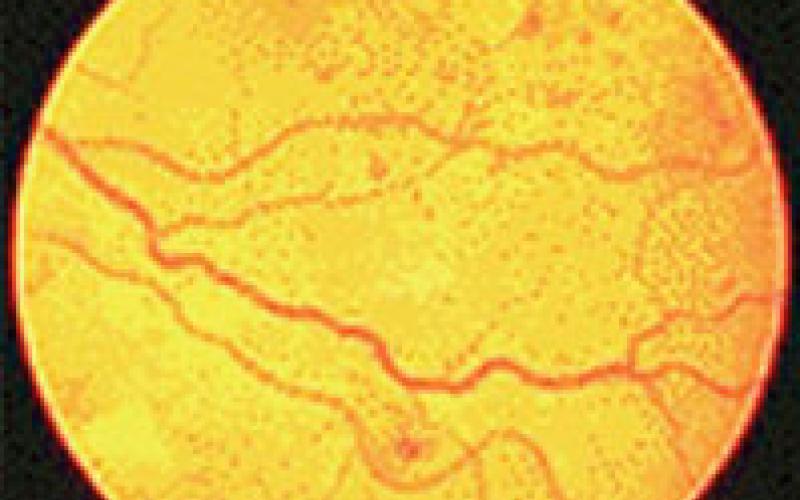
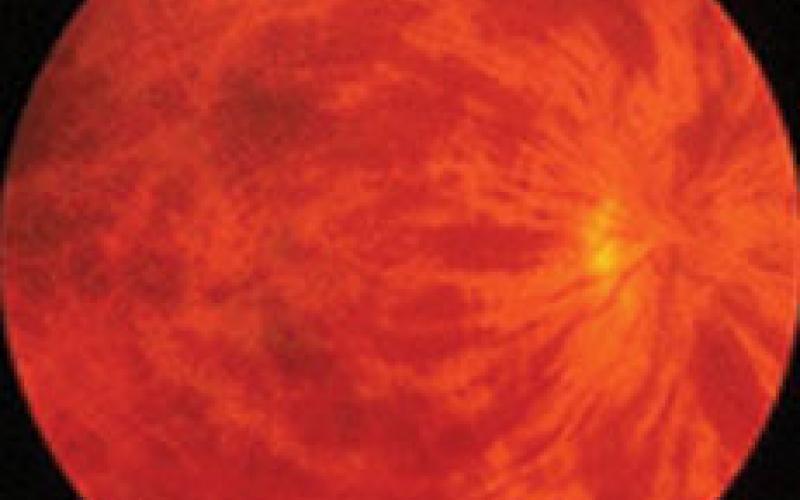
Early (nonproliferative) stage

Advanced (proliferative) stage
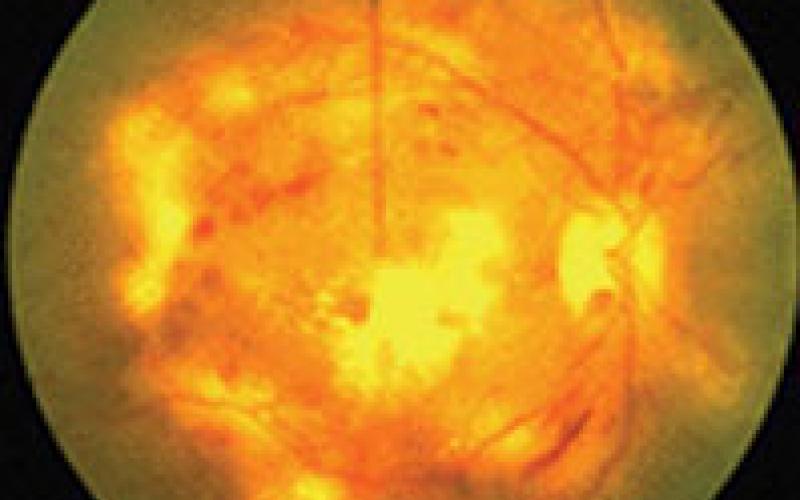
Advanced Macular Edema
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
The longer the life expectancy in society, the higher the rate of diseases related to old age. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the largest portion of vision loss in patients over 65 years of age. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is more common in smokers, patients with high blood pressure and cholesterol. There are two main types of AMD, dry type and wet type. Dry type causes slow vision loss over time. New type of vessel formation and bleeding caused by these vessels may cause distorted vision and sudden loss of vision. This can be detected by eye angiography (FFA) and by laser light tomography (OCT) of the eye.
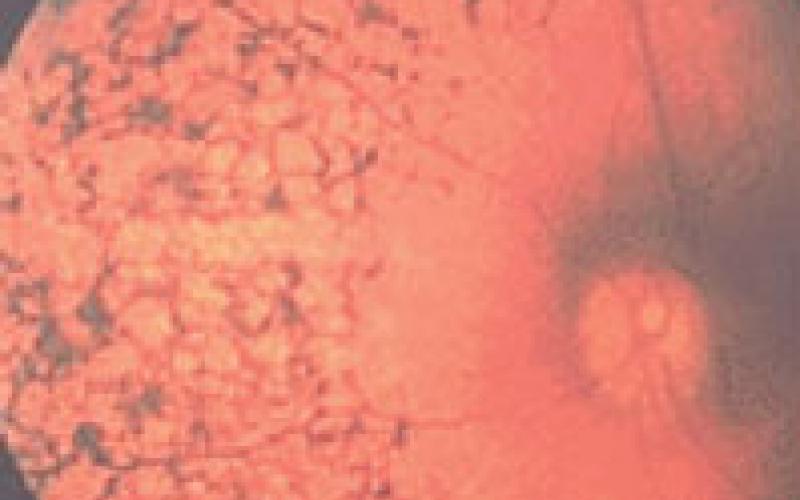

RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA
The most prominent feature of the disease is that patients cannot see well at night. Daytime vision may also diminish over time in advanced stages of the disease. Since it is a genetic disease, there is no known treatment.

